As governments ease lockdown restrictions, attention is focused on the risk of a second wave of COVID-19 infections. And, as JPMorgan writes, “the message from most people is: so far, so good, although as everyone also recognizes the lags with COVID-19 are long, so that three-to-four weeks need to pass in order to see how easing restrictions will impact new infections.”
Encouragingly, as JPM economist David Mackie points out, we have passed that point for a number of European countries. For example, Denmark started to ease lockdown restrictions 49 days ago without any sign of a second wave of infection. But, in JPM’s view, “this way of counting the days is misleading, and it will take a while longer before we know whether restrictions have been eased too much or not.”
In a report titled “Counting the days: risks of a COVID-19 second wave”, Mackie writes that the collapse in mobility when lockdown restrictions were imposed played a key role in driving the reproduction number (R-naught) below one. But, mobility has not been the only development weighing on the reproduction number, with JPM claiming that a number of other developments, including the buildup of immunity in the population, the reduced susceptibility of young people, the prospect of self-isolation of vulnerable individuals, the impact of weather and the impact of wearing masks and increased hygiene, all exert downward pressure on the reproduction number as mobility increases.
The bank’s analysis suggested that only when mobility increases more than halfway back from full-lockdown levels to pre-lockdown levels is there a risk of the reproduction number moving back above one. This suggests that, in assessing the risk of a second wave (or counting down the days to one), we should start counting the days from the moment that mobility in each country returns to the halfway mark.
This is what the JPM strategist has done in the table below, and it presents a much more cautious picture. As Mackie writes, “if we assume that it takes up to 28 days before we will see clear signs of a second wave, then only Norway and Denmark are close to that point. For the rest of Western Europe, we need to wait a while longer. Indeed, although mobility has increased in the United Kingdom and Italy since the lockdowns were eased, neither country has seen it return to the halfway mark.”
Receive a daily recap featuring a curated list of must-read stories.
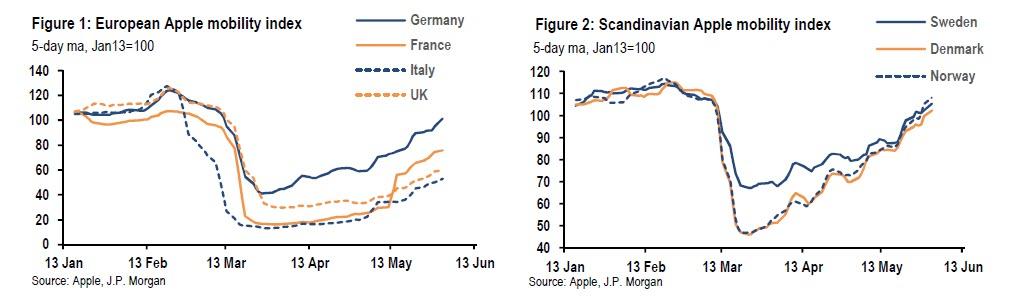
The bank’s conclusion: “A second wave of COVID-19 infection may or may not come to Western Europe. But it is much too early to assume that it won’t.”
One final note: we are confident that the largest US bank being one of the biggest beneficiaries of a new round of massive QE to be launched by the Fed if and when a second wave hits, had almost no impact on this analysis.
StevieRay Hansen
Editor, Bankster Crime
![]()




